This is Microsoft Technet article I just added some pictures.
Updated: February 1, 2009
This step-by-step example deployment, which uses a Windows Server 2008 certification authority (CA), contains procedures that guide you through the process of creating and deploying the public key infrastructure (PKI) certificates that Configuration Manager 2007 requires to operate in native mode. Native mode offers the highest level of security for a Configuration Manager 2007 site, and it is a requirement for Internet-based client management. For more information about native mode in Configuration Manager, see Benefits of Using Native Mode.
The procedures in this example refer to a Microsoft PKI solution, using an enterprise certification authority (CA) and certificate templates. The steps are appropriate for a test network only, as a proof of concept.
Because there is no single method of deployment for the required certificates, you will need to consult your particular PKI deployment documentation for the necessary procedures and best practices to deploy the required certificates for a production environment. For more information about the possible deployment methods, see Deploying the PKI Certificates Required for Native Mode.
| The use of a Microsoft PKI solution is recommended to support Configuration Manager 2007, but it is not required. Configuration Manager 2007 uses standard PKI certificates, supporting version 3 of the x.509 certificate format. If your existing PKI deployment can create, deploy, and manage the certificates that Configuration Manager 2007 requires for native mode, you can use your existing PKI infrastructure. Consult your PKI documentation for deployment details. |
In This Section
This example contains the following sections, which cover creating and deploying the basic certificates that are required for a Configuration Manager 2007 site to operate in native mode for intranet connectivity:
Deploying the Site Server Signing Certificate
Deploying the Web Server Certificate
Deploying the Client Certificate
Test Network Requirements
The example has the following requirements:
- The test network is running Active Directory Domain Services with Windows Server 2008, and it is installed as a single domain, single forest.
- You have a domain controller running Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition, which has installed on it the Active Directory Certificate Services role, and it is configured as an enterprise root certification authority (CA).
- You have one computer that has Windows Server 2008 (Standard Edition or Enterprise Edition) installed on it and that is designated as a member server, and you have Internet Information Services (IIS) installed on it.
- You have one Windows Vista client with the latest service pack installed, and this computer is configured with a computer name that comprises ASCII characters and is joined to the domain.
- You can log in with a root domain administrator account or an enterprise domain administrator account and use this account for all procedures in this example deployment.
Overview
PKI certificates must be installed prior to configuring Configuration Manager 2007 to operate in native mode. This example does not include installing and configuring Configuration Manager 2007, but it provides the steps to provision computers with the certificates they require to operate in Configuration Manager 2007 native mode.
The following table lists the three types of PKI certificates that are required and describes how they are used in a native mode Configuration Manager 2007 site:
| Certificate Requirement | Certificate Description |
| Site server signing certificate | This certificate is installed on the server that will be the Configuration Manager 2007 site server. It is used to sign client policies. |
| Web server certificate | This certificate is installed on servers that will be Configuration Manager 2007 site systems, with roles such as the management point and distribution point. It is used to encrypt data and authenticate the server to clients. |
| Client certificate | This certificate is installed on computers that will be Configuration Manager 2007 clients, and it is installed on the management point. It is used to authenticate the client to site systems; on the management point it is used to monitor the server's operational status. |
For more information about the certificates, see Certificate Requirements for Native Mode.
Follow the steps in this example to achieve the following goals:
- Provision the member server with a Configuration Manager 2007 site server signing certificate so that it can operate as a Configuration Manager 2007 site server in native mode.
- Provision the member server with a Web server certificate so that it can operate as a Configuration Manager 2007 site system server in native mode that can run any of these Configuration Manager site system roles: management point, distribution point, software update point, and state migration point.
- Provision a workstation and the member server with a client certificate so that the workstation can operate as a Configuration Manager 2007 native mode client, and so that the management point can report its status to the site server.
Deploying the Site Server Signing Certificate
This step has four procedures:
- Creating and Issuing the Site Server Signing Certificate Template on the Certification Authority
- Requesting the Site Server Signing Certificate for the Server That Will Run the Configuration Manager 2007 Site Server
- Approving the Site Server Signing Certificate on the Certification Authority
- Installing the Site Server Signing Certificate on the Server That Will Run the Configuration Manager 2007 Site Server
Creating and Issuing the Site Server Signing Certificate Template on the Certification Authority
To create and issue the site server signing certificate template
1. On the domain controller running the Windows Server 2008 console, click Start, click Programs, click Administrative Tools, and then click Certification Authority.
2. Expand the name of your certification authority (CA), and then click Certificate Templates.
3. Right-click Certificate Templates, and then click Manage to load the Certificates Templates Console.
4. In the results pane, right-click the entry that displays Computer in the Template Display Name column, and then click Duplicate Template.
5. In the Duplicate Template dialog box, ensure that Windows 2003 Server, Enterprise Edition is selected, and then click OK.
| Do not select Windows 2008 Server, Enterprise Edition. |
6. In the Properties of New Template dialog box, on the General tab, enter a template name for the site server signing certificate template, such as ConfigMgr Site Server Signing Certificate.
7. Click the Issuance Requirements tab, and then select CA certificate manager approval.
8. Click the Subject Name tab, and then click Supply in the request.
9. Click the Extensions tab, make sure Application Policies is selected, and then click Edit.
10. In the Edit Application Policies Extension dialog box, select Client Authentication, press Shift and select Server Authentication, and then click Remove.
11. In the Edit Application Policies Extension dialog box, click Add.
12. In the Add Application Policy dialog box, select Document Signing as the only application policy, and then click OK.
13. In the Properties of New Template dialog box, you should now see listed as the description of Application policies: Document Signing.
14. Click OK, click OK to close the Properties of New Template, and then close the Certificate Templates Console.
15. In the Certification Authority console, right-click Certificate Templates, click New, and then click Certificate Template to Issue.
16. In the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, select the new template you have just created, ConfigMgr Site Server Signing Certificate, and then click OK.
| If you cannot complete steps 15 or 16, check that you are using the Enterprise Edition of Windows Server 2008. Although you can configure certificate templates with Windows Server Standard Edition and Active Directory Certificate Services, you cannot deploy certificates using modified certificate templates unless you are using the Enterprise Edition of Windows Server 2008. |
17. Do not close the Certification Authority console.
Requesting the Site Server Signing Certificate for the Server That Will Run the Configuration Manager 2007 Site Server
To request the site server signing certificate
1. On the member server, create a folder to contain your certificate files.
2. Open Notepad, or a similar text file of your choice. Copy and paste the following text into the file:
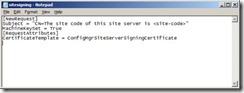
[NewRequest]
Subject = "CN=The site code of this site server is <site-code>"
MachineKeySet = True
[RequestAttributes]
CertificateTemplate = ConfigMgrSiteServerSigningCertificate
3. Replace the text <site-code> with your own site code. For example, if your site code is A01, the line will become: Subject = "CN=The site code of this site server is A01".
| Both the site code and the name of the template are case sensitive. Make sure that you specify the site code exactly as it appears in the Configuration Manager console, and that you specify the site server signing certificate template exactly as it appears as the Template name (not the Template display name) in the certificate template properties. |
4. Save the file with the name sitesigning.inf, and save it in the certificates folder that you created.
5. Open a command window in the certificates folder that you created, type the following command, and then press Enter:
certreq –new sitesigning.inf sitesigning.req
6. Type the following command, and then press Enter:
certreq –submit sitesigning.req sitesigning.cer
7. You are prompted to select the issuing CA in the Select Certification Authority dialog box. Select the CA, and then click OK. When the certificate is issued, you see RequestId: <number> displayed, where <number> is the next sequential certificate request to the issuing CA. Make a note of this number.
8. Do not close the command prompt.
Approving the Site Server Signing Certificate on the Certification Authority
To approve the site server signing certificate
1. On the domain controller, in Certification Authority, click Pending Requests.
2. In the results pane, you will see the requested certificate with the Request ID that was displayed with the last Certreq command.
3. Right-click the requested certificate, click All Tasks, and then click Issue.
4. Do not close the Certification Authority console.
Installing the Site Server Signing Certificate on the Server That Will Run the Configuration Manager 2007 Site Server
To retrieve and install the site server signing certificate
1. On the member server, in the command window, type the following command, and then press Enter:
certreq –retrieve <number> sitesigning.cer
For example, if the request number previously displayed was 12, type: certreq –retrieve 12 sitesigning.cer
2. You are prompted to select the issuing CA in the Select Certification Authority dialog box. Select the CA, and then click OK. Click OK to overwrite the existing file.
3. Type the following command, and then press Enter:
certreq –accept sitesigning.cer
The member server is now provisioned with a Configuration Manager 2007 site server signing certificate.
Deploying the Web Server Certificate
This step has four procedures:
- Creating a Windows Security Group for the Site System Servers
- Creating and Issuing the Web Server Certificate Template on the Certification Authority
- Requesting the Web Server Certificate
- Configuring IIS to Use the Web Server Certificate
Creating a Windows Security Group for the Site System Servers (Management Point, Distribution Point, Software Update Point, State Migration Point)
To create a Windows security group for the site system server
1. On the domain controller, click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and Computers.
2. Right-click the domain, click New, and then click Group.
3. In the New Object – Group dialog box, enter ConfigMgr IIS Servers as the Group name, and then click OK.
4. In Directory Users and Computers, right-click the group you have just created, and then click Properties.
5. Click the Members tab, and then click Add to select the member server.
| In our test environment, there is only one server to add. However, in a production environment, it is likely that various servers will host the Configuration Manager 2007 site systems that require certificates, such as the site's management point and distribution points. It is therefore good practice to assign permissions to a group and add the site systems that require the same type of certificate. Creating a security group for these servers enables you to assign permissions so that only these servers can use these certificates. |
6. Click OK, and then click OK again to close the group properties dialog box.
7. Restart your member server (if running) so that it can pick up the new group membership.
Creating and Issuing the Web Server Certificate Template on the Certification Authority
To create and issue the Web server certificate template on the certification authority
1. On the domain controller, while still running the Certification Authority console, right-click Certificate Templates and click Manage to load the Certificate Templates console.
2. In the results pane, right-click the entry that displays Web Server in the column Template Display Name, and then click Duplicate Template.
3. In the Duplicate Template dialog box, ensure that Windows 2003 Server, Enterprise Edition is selected, and then click OK.
| Do not select Windows 2008 Server, Enterprise Edition. |
4. In the Properties of New Template dialog box, on the General tab, enter a template name to generate the Web certificates that will be used on Configuration Manager site systems, such as ConfigMgr Web Server Certificate.
5. Click the Subject Name tab, click Build from this Active Directory information is selected, and then select one of the following for the Subject name format:
· Common name: Select this option if you will use fully qualified domain names for site systems in Configuration Manager (required for Internet-based client management, and recommended for clients on the intranet).
· Fully distinguished name: Select this option if you will not use fully qualified domain names in Configuration Manager.
6. Clear the option User principal name (UPN).
7. Click the Security tab, and remove the Enroll permission from the security groups Domain Admins and Enterprise Admins.
8. Click Add, enter ConfigMgr IIS Servers in the text box, and then click OK.
9. Select the Enroll permission for this group, and do not clear the Read permission.
10. Click OK, and close the Certificate Templates Console.
11. In the Certification Authority console, right-click Certificate Templates, click New, and then click Certificate Template to Issue.
12. In the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, select the new template you have just created, ConfigMgr Web Server Certificate, and then click OK.
13. Do not close the Certification Authority console.
Requesting the Web Server Certificate
To request the Web server certificate
1. Restart the member server to ensure it can access the certificate template with the configured permission.
2. Click Start, click Run, and type mmc.exe. In the empty console, click File, and then click Add/Remove Snap-in.
3. In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, select Certificates from the list of Available snap-ins, and then click Add.
4. In the Certificate snap-in dialog box, select Computer account, and then click Next.
5. In the Select Computer dialog box, ensure Local computer: (the computer this console is running on) is selected, and then click Finish.
6. In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, click OK.
7. In the console, expand Certificates (Local Computer), and then click Personal.
8. Right-click Certificates, click All Tasks, and then click Request New Certificate.
9. On the Before You Begin page, click Next.
10. On the Request Certificates page, select ConfigMgr Web Server Certificate from the list of displayed certificates, and then click Enroll.
11. On the Certificates Installation Results page, wait until the certificate is installed, and then click Finish.
12. Close Certificates (Local Computer).
Configuring IIS to Use the Web Server Certificate
To configure IIS to use the Web server certificate
1. On the member server, click Start, click Programs, click Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
2. Expand Sites, right-click Default Web Site, and then select Edit Bindings.
3. Click the https entry, and then click Edit.
4. In the Edit Site Binding dialog box, select the certificate that you requested by using the ConfigMgr Web Server Certificates template, and then click OK.
| If you are not sure which is the correct certificate, select one, and then click View. This allows you to compare the selected certificate details with the certificates that are displayed with the Certificates snap-in. For example, the Certificates snap-in displays the certificate template that was used to request the certificate. You can then compare the certificate thumbprint of the certificate that was requested with the ConfigMgr Web Server Certificates template with the certificate thumbprint of the certificate currently selected in the Edit Site Binding dialog box. |
5. Click OK in the Edit Site Binding dialog box, and then click Close.
6. Close Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
The member server is now provisioned with a Configuration Manager 2007 Web server certificate.
| If this server will be configured for software updates, there is additional IIS configuration that must be performed after WSUS is installed. For more information, see How to Configure the WSUS Web Site to Use SSL. |
Deploying the Client Certificate
This step has three procedures:
- Creating and Issuing the Workstation Authentication Certificate Template on the Certification Authority
- Configuring Autoenrollment of the Workstation Authentication Template Using Group Policy
- Automatically Enrolling the Workstation Authentication Certificate and Verifying Its Installation on Computers
Creating and Issuing the Workstation Authentication Certificate Template on the Certification Authority
To create and issue the Workstation Authentication certificate template on the certification authority
1. On the domain controller, while still running the Certification Authority console, right-click Certificate Templates, and then click Manage to load the Certificate Templates management console.
2. In the results pane, right-click the entry that displays Workstation Authentication in the column Template Display Name, and then click Duplicate Template.
3. In the Duplicate Template dialog box, ensure that Windows 2003 Server, Enterprise Edition is selected, and then click OK.
| Do not select Windows 2008 Server, Enterprise Edition. |
4. In the Properties of New Template dialog box, on the General tab, enter a template name to generate the client certificates that will be used on Configuration Manager client computers, such as ConfigMgr Client Certificate.
5. Click the Security tab, select the Domain Computers group, and select the additional permissions of Read and Autoenroll. Do not clear Enroll.
6. Click OK and close Certificate Templates Console.
7. In the Certification Authority console, right-click Certificate Templates, click New, and then click Certificate Template to Issue.
8. In the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, select the new template you have just created, ConfigMgr Client Certificate, and then click OK.
9. Close the Certification Authority console.
Configuring Autoenrollment of the Workstation Authentication Template Using Group Policy
To configure autoenrollment of the workstation authentication template using Group Policy
1. On the domain controller, click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Group Policy Management.
2. Navigate to your domain, right-click the domain, and then select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here.
| This step uses the best practice of creating a new Group Policy for custom settings rather than editing the Default Domain Policy that is installed with Active Directory Domain Services. By assigning this Group Policy at the domain level, you will apply it to all computers in the domain. However, on a production environment, you can restrict the autoenrollment so that it enrolls on only selected computers by assigning the Group Policy at an organizational unit level, or you can filter the domain Group Policy with a security group so that it applies only to the computers in the group. If you restrict autoenrollment, remember to include the server that is configured as the management point. |
3. In the New GPO dialog box, enter a name for the new Group Policy, such as Autoenroll Certificates, and click OK.
4. In the results pane, on the Linked Group Policy Objects tab, right-click the new Group Policy, and then click Edit.
5. In the Group Policy Management Editor, expand Policies under Computer Configuration, and then navigate to Windows Settings / Security Settings / Public Key Policies.
6. Right-click the object type named Certificate Services Client – Auto-enrollment, and then click Properties.
7. From the Configuration Model drop-down list, select Enabled, select Renew expired certificates, update pending certificates, and remove revoked certificates, select Update certificates that use certificate templates, and then click OK.
8. Close Group Policy Management.
Automatically Enrolling the Workstation Authentication Certificate and Verifying Its Installation on Computers
To automatically enroll the workstation authentication certificate and verify its installation on the client computer
1. Restart the workstation computer, and wait a few minutes before logging on.
| Restarting a computer is the most reliable method of ensuring success with certificate autoenrollment. |
2. Log on with an account that has administrative privileges.
3. In the search box, type mmc.exe., and then press Enter.
4. In the empty management console, click File, and then click Add/Remove Snap-in.
5. In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, select Certificates from the list of Available snap-ins, and then click Add.
6. In the Certificate snap-in dialog box, select Computer account, and then click Next.
7. In the Select Computer dialog box, ensure that Local computer: (the computer this console is running on) is selected, and then click Finish.
8. In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, click OK.
9. In the console, expand Certificates (Local Computer), expand Personal, and then click Certificates.
10. In the results pane, confirm that a certificate is displayed that has Client Authentication displayed in the Intended Purpose column, and that ConfigMgr Client Certificate is displayed in the Certificate Template column.
11. Close Certificates (Local Computer).
12. Repeat steps 1 through 11 for the member server to verify that the server that will be configured as the management point also has a client certificate.
The workstation and member server are now provisioned with a Configuration Manager 2007 client certificate.